
Qtum (pronounced as Quantum) is an open-source, public blockchain. The project has succeeded in gaining popularity thanks to its innovative solution to Bitcoin and Ethereum limitations. Additionally, the project’s token is one of the affordable cryptocurrencies listed among the first 100 assets at CoinMarketCap. The blockchain was founded in 2016 by Patrick Dai and launched in September 2017. Patrick has a master’s degree from the University of Sciences and Technology of China in the field of computer sciences.
He even applied for a Ph.D. in Communication and Information Systems but dropped out. Neil Mahi and Jordan Earls are the two co-founders and CTOs of Qtum. Neil is Qtum’s blockchain architect and has an MA degree in Business Administration but later shifted to computer science. Jordan is an experienced software developer and a well-known figure in the cryptocurrency domain; he is also a co-chair of the Smart Contracts Alliance. Unfortunately, there is little or no reliable information regarding the rest of the Qtum developers and engineers.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are the two most dominant assets in the cryptocurrency market, but they have deficiencies that have led to the development of many projects to address the problems. Qtum is one of the projects created to bring the best of Bitcoin and Ethereum into one place. However, unlike Bitcoin and Ethereum, which use Proof of Work (PoW) consensus, Qtum uses Proof of Stake (PoS) and has the upper hand in this regard, as explained below.
Moreover, Qtum uses Bitcoin’s UTXO transaction model and combines it with Ethereum’s capability to develop and run DApps. Overall, Qtum aims to address four major issues, namely interoperability (inter-blockchain data transfer), governance (project’s objectives management), rigidity (lack of flexibility in PoW consensus), and the barriers in the way of connecting smart contracts with the application we regularly use.
How does Qtum Work?
Qtum combines Bitcoin’s Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model and Ethereum’s Virtual machine. Qtum has created a protocol called (Account Abstraction Layer) which has made it compatible with various blockchains. Moreover, the project uses x86 Virtual Machine and supports other VMs, including Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM), meaning that any dApp developed on the Ethereum blockchain can be run in Qtum as well. The essence of x86 VM is the implementation of existing compilers and programming languages in Qtum without having to change the core elements of an app. Programmers can use the platform to develop utilities such as search engines, social network apps, payment apps, etc.
How is Qtum Better than BTC and ETH?
Qtum uses PoS consensus. Generally, consensuses are designed for the validity and safety of transactions in blockchain networks where there is no central authority to keep a ledger of the transactions. In other words, without a consensus, transactions cannot be verified, and the blockchain is subject to cyber-attacks. PoW and PoS are two instances of consensus mechanisms. In a PoW blockchain, new blocks are created in exchange for solving extremely difficult computational puzzles, which necessitate tremendous energy consumption.
The new blocks can then validate the transactions in the blockchain. On the other hand, PoS-based blockchains allow miners who have staked more of a given asset to confirm the transactions and receive transaction fees in return, cutting down on electricity. Qtum is built upon PoS, making it a relatively energy-efficient asset and friendly to the environment.
What are the Benefits of Qtum?
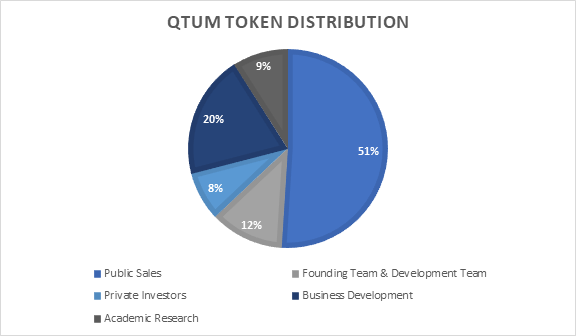
The asset has a maximum supply of 100 million tokens (97% of which have already been minted), meaning that Qtum is a deflationary cryptocurrency. Better yet, 51% of the max supply is dedicated to public sales, and its revenue is used to fund the project to keep it up and running. In addition, the 51% public share gives holders the right to vote on proposals such as changing the network’s block size or fees and the confidence that the project is not in full control of the founding team. Also, the remaining amount is distributed among private investors, the development team, the research staff, and the business team. The following chart from the Qtum whitepaper illustrates the distribution of the assets:
The second merit of Qtum is the project’s compatibility with implementing apps from various blockchains. Thanks to the AAL protocol and the x86 virtual machine, Ethereum-based apps can migrate to Qtum without losing scalability and modifying the underlying architecture.
Another strength of the project is its customized PoS consensus called the Mutualized Proof of Stake (MPoS). The combination of PoS and smart contracts can be susceptible to ‘junk contract’ attacks. The MPoS consensus enormously decreases the likelihood of such attacks by distributing the mining rewards between the new-block miner and the last nine miners (each receiving 10%), and the remaining rewards are delayed by 500 blocks. In short, the MPoS is designed to increase the security of the Qtum ecosystem.
What are the Drawbacks of Qtum?
The first problem is that the project has not determined a minimum amount for staking, and those who stake a relatively small amount of the asset can verify malicious transactions in the blockchain. However, with small amounts, it is less likely that the staker can mine the next new block. The second concern arises from the similarity between EVM and x86 VM. Solidity (EVM’s programing language) is still developing, and every now and then, a bug shows up in the dApps developed by EVM. Since EVM-based dApps can be launched in x86 VM, the Qtum platform can be susceptible to similar breakdowns despite the functionality brought about to the project by the AAL protocol.
Final Words
Qtum has provided an environment where Ethereum dApps can use Bitcoin’s UTXO model by relying on an experienced team of developers. Also, the blockchain uses MPoS which is more secure than PoS and power-efficient than PoW. All in all, the project has excellent potential, considering that it can resist the challenges EVM has faced through the course of its development.
Please note the above info is gathered solely for educatory purposes and is by no means financial advice.
Official Website: www.qtum.org
Alert Message